We, Greenish Land Co. would be so pleased to draw your attention to primitive definitions of measurement and instrumentation knowledge, before entering in details; following definitions instruct us to have an effective cognition about principles of measurement.
Process: a series of actions contain one of bellows changes happened or in order to achieve a result
- Change in energy level : liquid to gas conversion or chilling liquid
- Change in compositions: a chemical actions and reactions or making a mixture of different substances
- Change in articles size: grinding
Parameter: there is at least one factor in existence in each process would be measured or checked, such as flow, pressure, tank level, temperature, density, pH, viscosity, displacement, velocity or acceleration. Each one was known as parameter.
Instrument: each tool or device could be used in one of the following purposes are named process instrument.
- Measurement: discovering value of a parameter by measuring. Recognition, re-calculation, compensation function and alarms may be contained in a measuring package.
- Control: to order, limit, or rule something, or someone's actions or behavior. A device controls a process named as controller.
- Operator: a system or devices has been activated for a defined action based on a command received from controller.
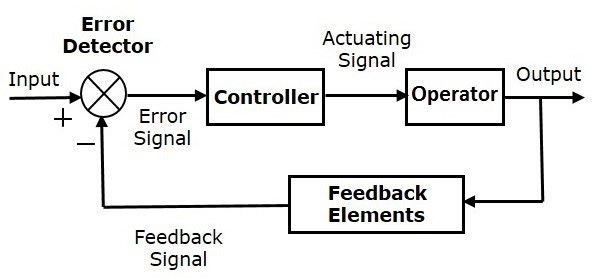
Sensor: a part of a measuring device faced measured parameter directly and reacts against its variation.
Convertor: a device receives a standard input and generates another type of standard output.
Transmitter: a convertor receives a measured parameter from sensor or sensing element, next converts to standard signal and conveys to another instruments as output. The output is a function of measured parameter only.
Convertor: a device receives a standard input and generates another type of standard output.
Transmitter: a convertor receives a measured parameter from sensor or sensing element, next converts to standard signal and conveys to another instruments as output. The output is a function of measured parameter only.
Analogue signal: a continuous signal which assigned to only one measured parameter imposed on an electronic variable signal. The most famous analogue signals are 4 to 20 mA or 1 to 5 V.
Digital Signal: a signal that is being used to represent data as a sequence of discrete values; at any given time it can only take on one of a finite number of values. This contrasts with an analog signal, which represents continuous values; at any given time it represents a real number within a continuous range of values.
Range: the area of variation between upper and lower limits on a particular scale.
Span: mathematical difference between upper and lower measuring set points (reading value). It is a part of continuum with upper limit value at one end and lower limit value at other end.
URV: Upper Reading Value
LRV: Lower Reading value
Resolution: the smallest interval measurable value by an instrument; the resolving power
Uncertainty: measurement uncertainty is the expression of the statistical dispersion of the values attributed to a measured quantity; in the other word, uncertainty value suggests us if our measured parameter is in a trustable range or not.
Precision: we face the amount of variation in multiple measurements of the same factor. In the other word better precision means lower variation in measurements. It could be another Interpretation of accuracy. This point should be reminded; we cannot modify a device precision by calibration or more accurate adjustment.
Error: difference between values put on a measuring device accurately and output generated or indicated by the device.
Sensitivity: ratio between output variations of a measuring device to its input in stable condition.
Hysteresis: Maximum difference between measured values with the same rising and falling applied input, in multiple measurement or history of its long life.
Repeatability: the maximum difference in output when applying the same input twice in the same direction of rising or falling.
Calibration: A measurement instrument output assigning to a defined input to calculate location on scale for example maximum point on a pressure gauge, calculating measurement error or adjusting output signal on a transmitter
Reference instrument: A highly accurate device would be used to adjust or calibrate another measuring device with lower accuracy.
Farbod Tabesh - 18.07.2019