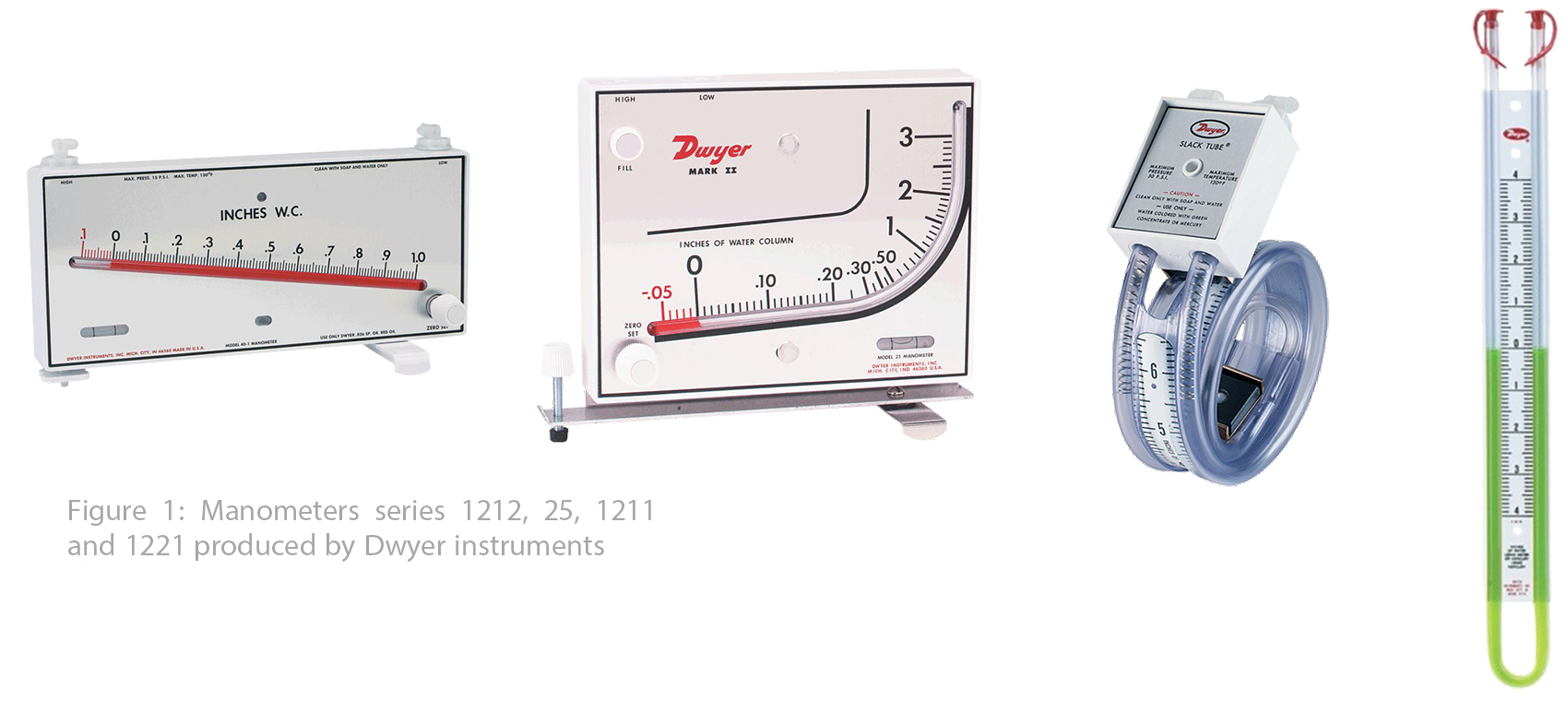
Physical pressure definition was used for pressure measurement for many years before bourdon gauges innovation, in other words using a column of liquid was the best indication of pressure value based on a famous equation P=ρgh and manometer as a symbol
As explained in pressure definitions, affect of pressure force on elastic part causes some difference in length, volume or dimension; as a result, pressure elastic tube was a great innovation.
More than one hundred seventy years have passed since the first pressure gauge innovation.
Eugène Bourdon was a French watch maker and engineer who introduced first pressure tube to transform pressure measurement methods and industrial world in 1849 ; an innovation could change measuring principals fundamentally; after that, his name linked with the new product and pressure tube's name has been replaced by Bourdon tube quickly.
 What is the function of a pressure instrument?
What is the function of a pressure instrument?
Pressure instrument is a mechanical or electrical device which gauge is a device measures pressure of gas, liquid or two phase fluids in a tanks, vessels, pipe lines or a process, pressure gauges, transmitters and switches; likewise, differential pressure gauges, switches and transmitters are generally categorized in pressure instruments.
What is a pressure gauge?
The optimal solution for wide range of industrial applications is a pressure gauge. An extensive portfolio of pressure gauges equipped with various technologies: Bourdon tube, capsule, diaphragm, bellows sensors allow to measure relative, absolute and differential pressure, available in stainless steel, copper, monel, among other special materials. Measuring ranges between 0 ... 4 mbar and 0 ... 1600 bar and class 0.25.
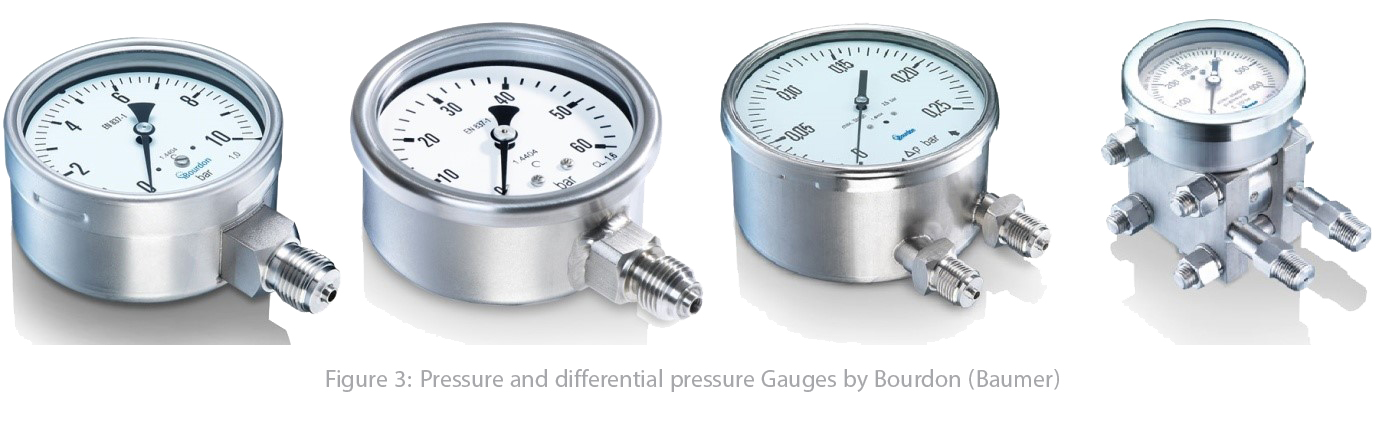 How many types of pressure gauge are available?
How many types of pressure gauge are available?
Pressure gauges are categorized in application and measuring range order as per following parts.
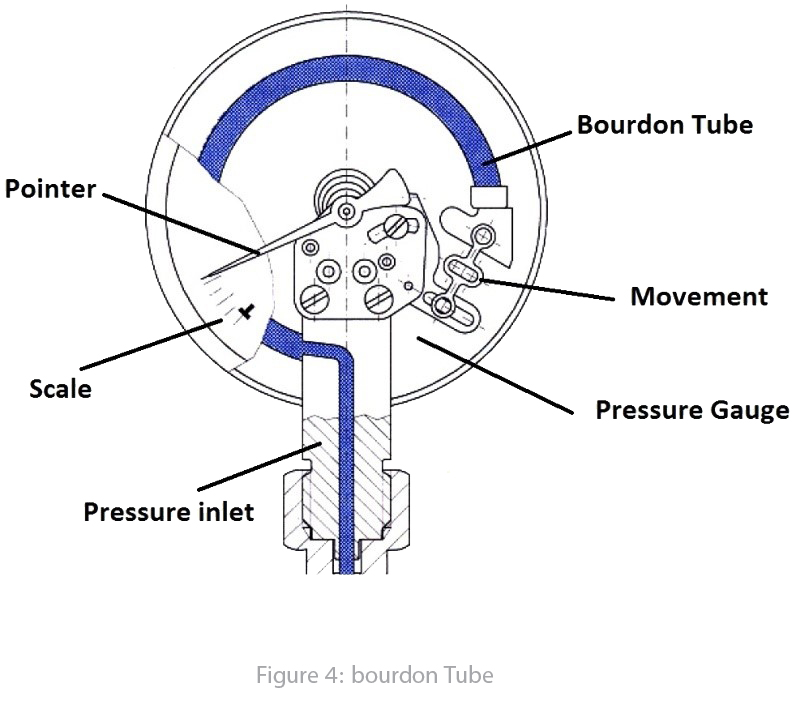
Bourdon tube: It is an empty tube formed like a "C" in 250°approximately. It works like a fixed end beam will bend and experience by shear deformation when a pressurized fluid entered inside the C tube thanks to Timoshenko beam theory. This deflection made a small movement for a gear mechanism connected to pointer; as a result, we are witness to pointer moving from zero to full scale by pressure increasing. A simple structure is mentioned in figure 3.
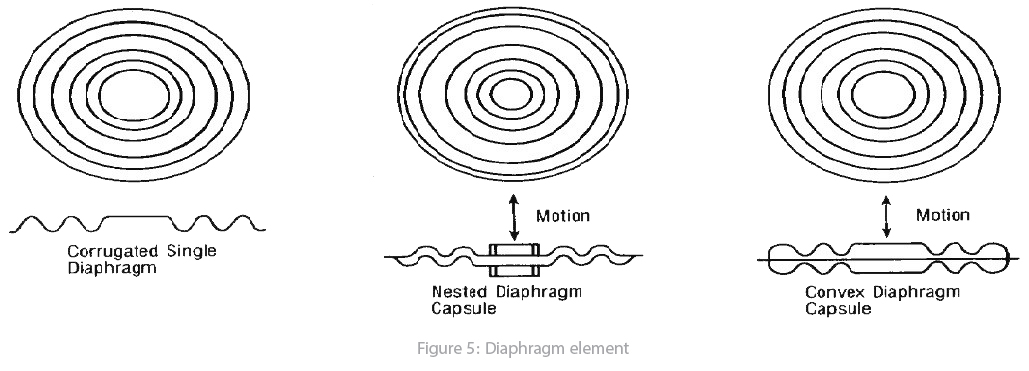
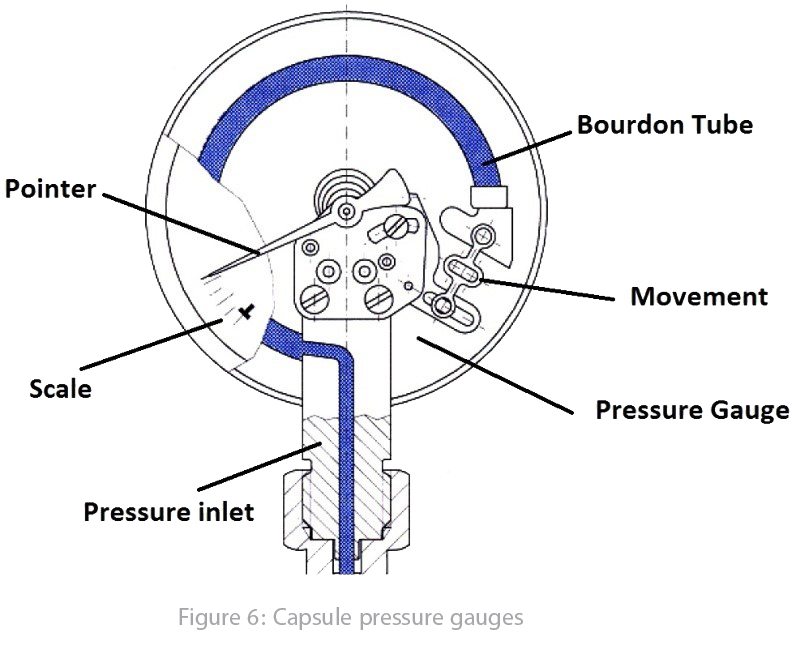
Capsule (diaphragm): It is an elastic part withstands pressure and deflected consequently. A rippling metallic disk (Figure 5) is used as the elastic part in most cases can be deflected by pressure increasing. Wide range of this element type application is pressure measurement in clean gases or air. Following picture explain the mechanism.
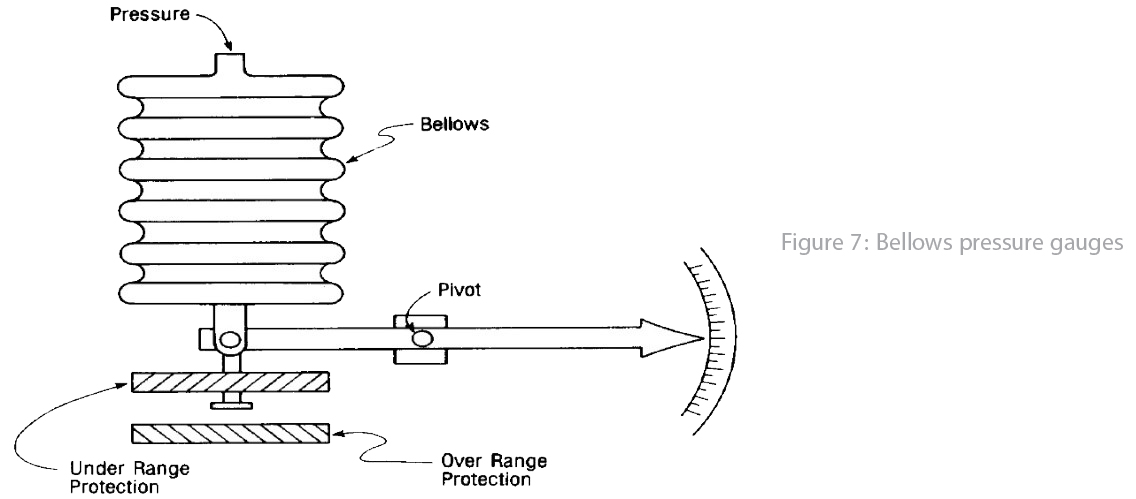
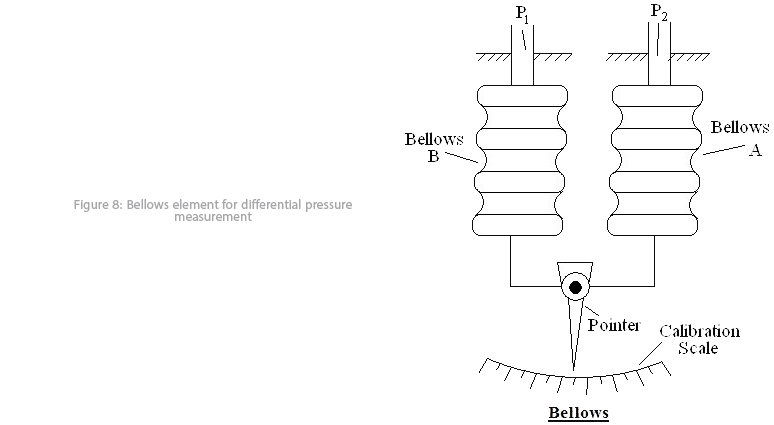
Bellow: We face an elastic part in this method also, like a diaphragm but out of rubber or steel. Usually, more than one diaphragms have been exploited in measuring element structure expand by pressure changes (figure 7); so it is more sensitive and applicable for very low pressure values; furthermore, it can be used for differential pressure measurement applications too (figure 8).
 Pressure gauge's specification in one view:
Pressure gauge's specification in one view:
- Dial size: 40, 63, 100, 150, 250 mm
- Measuring range: 6 mbar to 700 bar
- Over pressure: up to 750 bar
- Operating temperature range: -40 to +130 °C
- Accuracy class: 0.5 to 2% FS
- Connection material: SS / Alloy
- Process connections: Thread, Flange
- Measuring units: psi, bar, pa, atm, mmwc
Farbod Tabesh
August - 2019